
Oral Culture
Internet Archive, via Wikimedia Commons
Cooperative communication, collective planning and community decision-making, negotiation, rules and customs—all were made possible with the development of speech. For the first time, the interconnectedness of the group could be reinforced through the creation and repetition of stories and myths.
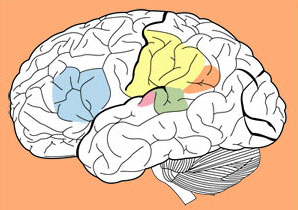
We don’t know exactly when hominids began using speech; it may have been as early as 200,000 years ago, and almost certainly had progressed by 50,000 years ago. When modern humans entered Europe about 45,000 to 42,000 years ago, Neanderthals were already there. The two groups lived side by side and competed for the same resources until Neanderthals died out, about 35,000 years ago. Some scholars believe that complex speech was the primary advantage modern humans had over Neanderthals, based on skull differences in the basicranial line, nasopharynx and upper vocal cavity.
Cultural Takeoff Propelled by Speech
Between 45,000 and 35,000 years ago, genetically modern humans achieved what anthropologist Marvin Harris in his book Our Kind calls cultural takeoff, which was almost certainly propelled by a linguistic takeoff. Based on anatomical evidence including an enlarged brain, a new, descended larynx and changes to the suboral cavity and tongue, both Harris and Merlin Donald believe that by at least 45,000 years ago Homo sapiens had fully developed speech and a complex oral culture.
By at least 45,000 years ago Homo sapiens had fully developed speech and a complex oral culture.
Speech was the ideal medium for developing symbolic communication among people who lived close together, without compromising the visual and motor skills they relied on for survival. For one thing, speech does not interfere with other activities such as locomotion, tool- or jewelry-making. People were able to talk to each other and communicate relevant information much more efficiently and at times when it would have been impossible to use mimesis.
Another advantage of speech is that the range of vocal sounds humans can produce to express themselves is substantially more than a usable repertoire of mimetic symbols or the limited number of sounds that apes can produce.
And lastly, speech is relatively easy to remember and rehearse, so a group could produce a large body of words that were retrievable in memory.
Oral Expression Is Innate in Babies
About 6,000 sounds represent the spoken languages around the world and babies can recognize all of them.
Helen Keller, an American woman who was deaf, dumb and blind from infancy, says in her autobiography that as a child she felt driven to vocalize, even though she could not hear her sounds and didn’t know that speech was for communicating. Although her family tried to discourage her from making what they thought of as random noise, she could not resist the sensation of vocalizing.
She also relates the incident when, after intensive efforts by her teacher to teach sign language to her, she suddenly recognized what it all meant: that everything has a name. This was the very powerful mental model that united sign language and the world of experience for her, and it is likely a basic model for the understanding of all symbolic languages.
How the Expression of Advanced Concepts Evolved

Donald and others believe that the evolution of speech was driven by our desire to communicate concepts we could not express through mimesis. Beyond the simple relating of here-and-now events and circumstances, the need for cooperative communication, to make collective plans and community decisions, to negotiate, create rules and customs, all these needs were met with speech.
For the first time stories and myths were created and repeated which helped to reinforce the interconnectedness of the group. All Stone Age cultures that have survived into the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries have highly developed mythic/religious traditions. This separated modern humans from their ancestors who did not have speech.
In predominantly oral societies, myth is the main controlling social force, assigning meaning, context and setting to every act, event, object and creature. We think of these early cultures with speech as oral societies, because the facility of speech dominated and profoundly affected the nature of their group interactions.

The First Word
The Search for the Origins of Language
Christine Kenneally
Human communication depends on the same genetic foundations as other animals. Some were born with a greater inclination to collaborate, forming the symbolic communication of language.

Numbers and the Making of Us
Counting and the Course of Human Cultures
Caleb Everett
Numbers, says Everett, are a key linguistic innovation that has distinguished our species and reshaped human experience.
